250128 'GNAX' http://farbe.li.tu-berlin.de/CEA_I.HTM or http://color.li.tu-berlin.de/CEA_I.HTM.
'CNAX':@PROZ_CEA_I.COM format: 'dmyy'LINKSEA_H.HTM
Go to this page in German CGA_I.HTM
Chapter A:
Colour Image Technology and Colour Management (2019)
Introduction, content list and summary:
AEAI,
AEA_I,
AEA_S in English or
AGAI,
AGA_I,
AGA_S in German.
Image pages with 10 and 260 image series:
AEAS,
ae2s in English or
AGAS,
ag2s in German.
Chapter B:
Colour Vision and Colorimetry (2020)
Introduction, content list and summary:
BEAI,
BEA_I,
BEA_S in English or
BGAI,
BGA_I,
BGA_S in German.
Image pages with 10 and 260 image series:
BEAS,
be2s in English or
BGAS,
bg2s in German.
Chapter C:
Colour Spaces, Colour Differences, and Line Elements (2021)
Introduction, content list and summary:
CEAI,
CEA_I,
CEA_S in English or
CGAI,
CGA_I,
CGA_S in German.
Image pages with 10 and 260 image series:
CEAS,
ce2s in English or
CGAS,
cg2s in German.
Chapter D:
Colour Appearance, Elementary Colours, and Metrics (2022)
Introduction, content list and summary:
DEAI,
DEA_I,
DEA_S in English or
DGAI,
DGA_I,
DGA_S in German.
Image pages with 10 and 260 image series:
DEAS,
de2s in English or
DGAS,
dg2s in German.
Chapter E:
Colour Metrics, Differences, and Appearance (2023)
Introduction, content list and summary:
eeai,
eea_i,
eea_s in English or
egai,
ega_i,
ega_s in German.
Image pages with 10 and 260 image series:
eeas,
ee2s in English or
egas,
eg2s in German.
Chapter F:
Colour metrics for chromatic and luminance adaptation (2024)
Introduction and content list:
feai,
fea_i in English or
fgai (under work),
fga_i in German.
Image pages with 10 and 260 image series:
feas,
fe2s in English or
fgas,
fg2s in German.
Chapter G:
Equally spaced colour scales for optimal colour-image quality (2024b)
Content list:
gea_i in English or
gga_i in German.
Image pages with 10 and 260 image series:
geas
ge2s in English or
ggas,
gg2s in German.
Chapter H:
SDR and HDR-colour metric for optimal colour-image quality (2025)
Content list:
hea_i in English or
hga_i in German.
Image pages with 10 (and 260, under work) image series:
heas
he2s in English or
hgas,
hg2s in German.
Chapter I:
Output linearization of visual data for scaling and thresholds (2025b)
, under work
Content list:
iea_i in English or
iga_i in German.
Image pages with 10 (and 260, under work) image series:
ieas
ie2s in English or
igas,
ig2s in German.
Remarks:
Any large image file with 260 pages, for example
he2s.htm,
can be printed as image series.
Also the content can be saved as a pdf file for any of the chapters A to H.
In addition a download of the corresponding pdf file, for example
he2s.pdf (about 150MB) is possible.
Project title: Colour and colour vision with Ostwald, device, and elementary colours -
Antagonistic colour-vision model TUBJND and properties for many applications
Chapter C: Colour Spaces, Colour Differences, and Line Elements (2021),
Main part CEA_I
Each chapter includes main parts (I) with information to an image part (S).
There are 26 image parts (S), each with 10 figure pages.
The 10 figure pages (0 to 9) include up to 16 figures,
and each figure with up to six formats.
Structure, content, and order of files and figures on the example chapter
Colour Vision and Colorimetry
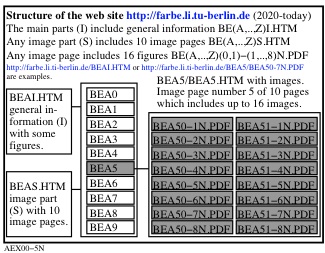
Figure 1 shows the structure of the web site BE(A..Z)I.HTM und BE(A..Z)S.HTM.
For the download of this figure in the VG-PDF format, see
AEX00-5N.PDF.
Structure, content, and order of files and figures on the web site
http://farbe.li.tu-berlin.de.
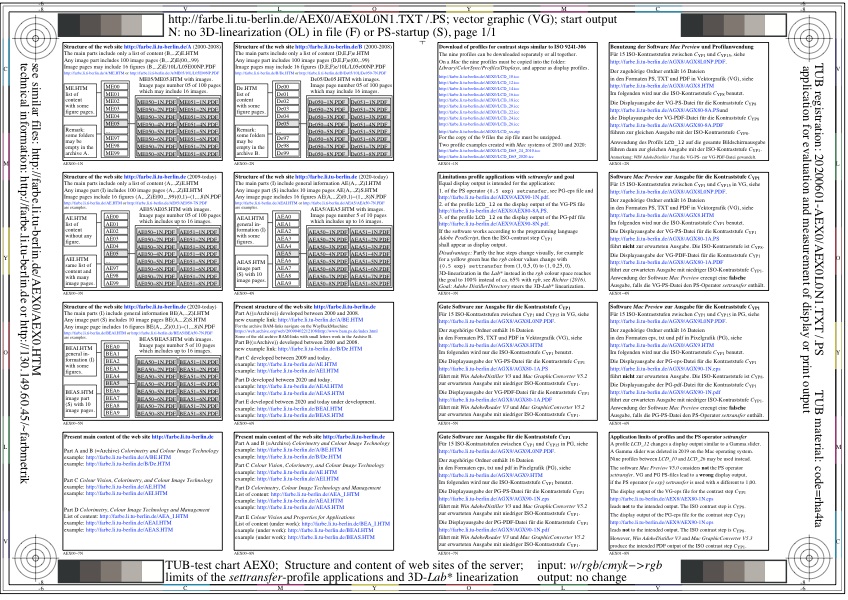
Figure 2 shows the structure, the content, and the order of files and figures on the web site
http://farbe.li.tu-berlin.de.
For the download of this figure in the VG-PDF format, see
AEX0L0N1.
List of links to the contents of all image parts
Image part CEAS
in English or CGAS in German.
Title: Line elements, colour spaces, and colour thresholds;
Comparison of LABJND and CIELAB line elements.
1. Introduction and goals.
2. Line elements for achromatic colours;
3. Colour spaces and chromatic thresholds;
4. Relation of the laws of Weber-Fechner & Stevens.
5. LABJND-line elements according to CIE 230:219;
6. Comparison with CIELAB-line elements according to ISO/CIE 11664-4.
for further information and discussion,
see CEAI.
go to the image part CEAS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part CEBS
in English or CGBS in German.
Title: Colour thresholds and line elements in 10 colour spaces
LABJNDu0 to 9, A0n=1,5
1. Introduction and goals;
2. Modifications LABJNDu0 to 9 of the colour difference formula LABJND
according to CIE 230:2019;
3. Corresponding line elements for the experimental contrast
Y/(delta Y);
4. Absolute lightness L* (CIE 15) and T* (IEC sRGB)
and relative lightness l* and t*;
5. Logarithmic and linear figures for L*, T*, l* and t*;
6. Logarithmic figures for threshold delta Y, sensitivity
(delta Y)/Y, and contrast Y/(delta Y);
7. Parameters: A0n=1,5, A1n=sv*cx, A2n=cv*cx, sv=0,0170, cv=0,0058, cx=1,00;
8. Variations cx=0,84, 0,67 und 0,42, and additional data.
go to the image part CEBS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part CECS
in English or CGCS in German.
Title: Colour thresholds and line elements in 10 colour spaces
LABJNDu0 to 9
1. Introduction and goals;
2. Modifications LABJNDu0 to 9 of the colour difference formula LABJND
according to CIE 230:2019;
3. Corresponding line elements for the experimental contrast
Y/(delta Y);
4. Absolute lightness L* (CIE 15) and T* (IEC sRGB)
and relative lightness l* and t*;
5. Logarithmic and linear figures for L*, T*, l* and t*;
6. Logarithmic figures for threshold delta Y, sensitivity
(delta Y)/Y, and contrast Y/(delta Y);
7. Parameters: A0n=1,5, A1n=sv*cx, A2n=cv*cx, sv=0,0170, cv=0,0058, cx=1,00;
8. Variations cx=0,84, 0,67 und 0,42.
go to the image part CECS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part CEDS
in English or CGDS in German.
Title: Colour thresholds and line elements in 10 colour spaces
LABJNDu0 to 9
1. Introduction and goals;
2. Modifications LABJNDu0 to 9 of the colour difference formula LABJND
according to CIE 230:2019;
3. Corresponding line elements for the experimental contrast
Y/(delta Y);
4. Absolute lightness L* (CIE 15) and T* (IEC sRGB)
and relative lightness l* and t*;
5. Logarithmic and linear figures for L*, T*, l* and t*;
6. Logarithmic figures for threshold delta Y, sensitivity
(delta Y)/Y, and contrast Y/(delta Y);
7. Parameters: A0n=1,0, A1n=sv*cx, A2n=cv*cx, sv=0,0170, cv=0,0058, cx=1,00;
8. Variations cx=0,84, 0,67 und 0,42, and additional data.
go to the image part CEDS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part CEES
in English or CGES in German.
Title: Colour thresholds and line elements in 10 colour spaces
LABJNDu0 to 9
1. Introduction and goals;
2. Modifications LABJNDu0 to 9 of the colour difference formula LABJND
according to CIE 230:2019;
3. Corresponding line elements for the experimental contrast
Y/(delta Y);
4. Absolute lightness L* (CIE 15) and T* (IEC sRGB)
and relative lightness l* and t*;
5. Logarithmic and linear figures for L*, T*, l* and t*;
6. Logarithmic figures for threshold delta Y, sensitivity
(delta Y)/Y, and contrast Y/(delta Y);
7. Parameters: A0n=1,5, A1n=sv, A2n=cv*cx, sv=0,0170, cv=0,0058, cx=1,00;
8. Variations cx=0,84, 0,67 und 0,42, and additional data.
go to the image part CEES
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part CEFS
in English or CGFS in German.
Title: Colour thresholds and line elements in 10 colour spaces
LABJNDu0 to 9
1. Introduction and goals;
2. Modifications LABJNDu0 to 9 of the colour difference formula LABJND
according to CIE 230:2019;
3. Corresponding line elements for the experimental contrast
Y/(delta Y);
4. Absolute lightness L* (CIE 15) and T* (IEC sRGB)
and relative lightness l* and t*;
5. Logarithmic and linear figures for L*, T*, l* and t*;
6. Logarithmic figures for threshold delta Y, sensitivity
(delta Y)/Y, and contrast Y/(delta Y);
7. Parameters: A0n=1,5, A1n=sv, A2n=cv*cx, sv=0,0170, cv=0,0058, cx=1,00;
8. Variations cx=0,84, 0,67 und 0,42.
go to the image part CEFS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part CEGS
in English or CGGS in German.
Title: Colour thresholds and line elements in 10 colour spaces
LABJNDu0 to 9
1. Introduction and goals;
2. Modifications LABJNDu0 to 9 of the colour difference formula LABJND
according to CIE 230:2019;
3. Corresponding line elements for the experimental contrast
Y/(delta Y);
4. Absolute lightness L* (CIE 15) and T* (IEC sRGB)
and relative lightness l* and t*;
5. Logarithmic and linear figures for L*, T*, l* and t*;
6. Logarithmic figures for threshold delta Y, sensitivity
(delta Y)/Y, and contrast Y/(delta Y);
7. Parameters: A0n=1,5, A1n=sv*cx, A2n=cv, sv=0,0170, cv=0,0058, cx=1,00;
8. Variations cx=0,84, 0,67 und 0,42, and additional data.
go to the image part CEGS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part CEHS
in English or CGHS in German.
Title: Colour thresholds and line elements in 10 colour spaces
LABJNDu0 to 9
1. Introduction and goals;
2. Modifications LABJNDu0 to 9 of the colour difference formula LABJND
according to CIE 230:2019;
3. Corresponding line elements for the experimental contrast
Y/(delta Y);
4. Absolute lightness L* (CIE 15) and T* (IEC sRGB)
and relative lightness l* and t*;
5. Logarithmic and linear figures for L*, T*, l* and t*;
6. Logarithmic figures for threshold delta Y, sensitivity
(delta Y)/Y, and contrast Y/(delta Y);
7. Parameters: A0n=1,5, A1n=sv*cx, A2n=cv, sv=0,0170, cv=0,0058, cx=1,00;
8. Variations cx=0,84, 0,67 und 0,42.
go to the image part CEHS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part CEIS
in English or CGIS in German.
Title: 8 basic colours RYGCBMNW and 16 grey steps,
Change of the colour data by up to 8 diplay reflexions
1. Introduction and goals.
2. Change of the colour data for 8 basic colours;
3. Change of the colour data for 16 grey steps;
4. Colour data rgb*, LabC*h and w for up to 8 reflexions.
go to the image part CEIS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part CEJS
in English or CGJS in German.
Title: Relative antagonistic colour vision model LMS-R21,
illuminant E00
1. Introduction and goals.
2. Linear sensitivities and linear differences;
calculated model data marked with dashed lines (DL);
without and with thresholds tsa=0,00 and 0,10.
3. Ten triple combinations of maximal sensitivities: (545,557,570) and;
30. (545,570,595), (520,570,620), DL;
31. (495,520,545), (470,520,570), DL;
32. (445,470,495), (420,470,520), DL;
33. (570,595,620), (520,570,620);
34. (545,570,595), (520,570,620);
35. (520,545,570), (520,570,620);
36. (495,520,545), (470,520,570);
37. (470,495,520), (470,520,570);
38. (445,470,495), (420,470,520);
39. (420,445,470), (420,470,520);
4. Figures of linear spectral sensitivities
and linear differences.
for further information and discussion,
see CEAJ.
go to the image part CEJS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part CEKS
in English or CGKS in German.
Title: Relative antagonistic colour vision model LMS-R21,
illuminant E00
1. Introduction and goals.
2. Logarithmic sensitivities and logarithmic differences;
calculated model data marked with dashed lines (DL);
without and with thresholds tsa=0,00 and 0,10.
3. Ten triple combinations of maximal sensitivities: (545,557,570) and;
30. (545,570,595), (520,570,620), DL;
31. (495,520,545), (470,520,570), DL;
32. (445,470,495), (420,470,520), DL;
33. (570,595,620), (520,570,620);
34. (545,570,595), (520,570,620);
35. (520,545,570), (520,570,620);
36. (495,520,545), (470,520,570);
37. (470,495,520), (470,520,570);
38. (445,470,495), (420,470,520);
39. (420,445,470), (420,470,520);
4. Figures of logarithmic spectral sensitivities
and logarithmic differences.
go to the image part CEKS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part CELS
in English or CGLS in German.
Title: Relative antagonistic colour vision model LMS-R21,
illuminant E00
1. Introduction and goals.
2. Logarithmic sensitivities and linear differences;
calculated model data marked with dashed lines (DL);
without and with thresholds tsa=0,00 and 0,10.
3. Ten triple combinations of maximal sensitivities: (545,557,570) and;
30. (545,570,595), (520,570,620), DL;
31. (495,520,545), (470,520,570), DL;
32. (445,470,495), (420,470,520), DL;
33. (570,595,620), (520,570,620);
34. (545,570,595), (520,570,620);
35. (520,545,570), (520,570,620);
36. (495,520,545), (470,520,570);
37. (470,495,520), (470,520,570);
38. (445,470,495), (420,470,520);
39. (420,445,470), (420,470,520);
4. Figures of logarithmic spectral sensitivities
and linear differences.
go to the image part CELS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part CEMS
in English or CGMS in German.
Title: Four CIE colorimetries and some relations to the
antagonistic relative colorimetry R21.
1. Introduction and goals.
2. Linear CIE sensitivities and CIE differences
without thresholds tsa=0,00.
3. Combinations of CIE illuminant and CIE colorimetry;
30. D65 and HPE-CIE-02;
31. D65 and HPE-CIE-10;
32. E00 and HPE-CIE-02;
33. E00 and HPE-CIE-10;
34. E00 and LMS-CIE-F02;
35. E00 and LMS-CIE-F10;
36. D50 and HPE-CIE-02;
37. D50 and HPE-CIE-10;
38. D50 and LMS-CIE-F02;
39. D50 and LMS-CIE-F10.
go to the image part CEMS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part CENS
in English or CGNS in German.
Title: Four CIE colorimetries and some relations to the
antagonistic relative colorimetry R21.
1. Introduction and goals.
2. Linear CIE sensitivities and CIE differences
without thresholds tsa=0,00.
3. Combinations of CIE illuminant and CIE colorimetry.
30. D65 and HPE-CIE-F02;
31. D65 and HPE-CIE-F10;
32. P00 and HPE-CIE-02;
33. P00 and HPE-CIE-10;
34. P00 and LMS-CIE-F02;
35. P00 and LMS-CIE-F10;
36. Q00 and HPE-CIE-02;
37. Q00 and HPE-CIE-10;
38. Q00 and LMS-CIE-F02;
39. Q00 and LMS-CIE-F10.
go to the image part CENS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part CEOS
in English or CGOS in German.
Title: Four CIE colorimetries and some relations to the
antagonistic relative colorimetry R21.
1. Introduction and goals.
2. Linear CIE sensitivities and CIE differences
without thresholds tsa=0,00.
3. Combinations of CIE illuminant and CIE colorimetry.
30. E00 and LMS-CIE-F02 with basic raltions;
31. E00 and LMS-CIE-F10 with basic relations;
32. Eight illuminants Dxx and HPE-CIE-02;
33. Eight illuminants Dxx and HPE-CIE-10;
34. Eight illuminants Dxx and LMS-CIE-F02;
35. Eight illuminants Dxx and LMS-CIE-F10;
36. Eight illuminants Pxx and HPE-CIE-02;
37. Eight illuminants Pxx and HPE-CIE-10;
38. Eight illuminants Pxx and LMS-CIE-F02;
39. Eight illuminants Pxx and LMS-CIE-F10.
go to the image part CEOS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part CEPS
in English or CGPS in German.
Title: LMS-R21 Colour-vision model, lin[threshold]=0 & 0,04 & 0,10;
lin[sensitivity] and lin[ratio]
1. Introduction and goals.
2. Cone ratio L:M:S, saturation V;
3. Sensitivities LMV->L/V & M/V and OLM->O/L & M/L;
4. Four adaptations: 620,570,520,470 and 595,570,545,520;
5. Sensitivity 557,457,507, VNg->V/g & N/g, WN-antigonisme;
6. Sensitivity 570,470,520, LBG->L/G & B/G, YB-antigonisme.
go to the image part CEPS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part CEQS
in English or CGQS in German.
Title: LMS-R21 Colour-vision model, lin[threshold]=0 & 0,04 & 0,10;
log[sensitivity] and log[ratio]
1. Introduction and goals.
2. Cone ratio L:M:S, saturation V;
3. Sensitivities LMV->L/V & M/V and OLM->O/L & M/L;
4. Four adaptations: 620,570,520,470 and 595,570,545,520;
5. Sensitivity 557,457,507, VNg->V/g & N/g, WN-antigonisme;
6. Sensitivity 570,470,520, LBG->L/G & B/G, YB-antigonisme.
go to the image part CEQS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part CERS
in English or CGRS in German.
Title: LMS-R21 Colour-vision model, lin[threshold]=0 & 0,04 & 0,10;
lin & log [sensitivity & ratio]
1. Introduction and goals.
2. Cone ratio L:M:S, saturation V;
3. Sensitivities LMV->L/V & M/V and OLM->O/L & M/L;
4. Four adaptations: 620,570,520,470 and 595,570,545,520;
5. Sensitivity 557,457,507, VNg->V/g & N/g, WN-antigonisme;
6. Sensitivity 570,470,520, LBG->L/G & B/G, YB-antigonisme.
go to the image part CERS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part CESS
in English or CGSS in German.
Title: Special properties of colour vision;
Lightness, threshold, sensitivity and contrast functions
1. Introduction and goals.
2. Basic functions for visual thresholds and attributes;
3. Logarithmic and linear functions of colour vision attributes;
3. CIELAB, CIEDE2000, and LABJND colour-difference formulae;
4. Comparison results of the different formulae;
5. Short time and long time viewing of colour samples.
go to the image part CESS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part CETS
in English or CGTS in German.
Title: Special properties of colour vision;
Input and output linearization with ISO-colour files;
Lightness, threshold, sensitivity and contrast functions
1. Introduction and goals.
2. Basic functions for visual thresholds and attributes;
3. Logarithmic and linear functions of colour vision attributes;
3. CIELAB, CIEDE2000, and LABJND colour-difference formulae;
4. Comparison results of the different formulae;
5. Use of ISO files according to ISO 9241-306:2019 and ISO/IEC 15775:2022;
6. Input and output linearisation: ISO file -> print -> scan -> ISO file.
go to the image part CETS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part CEUS
in English or CGUS in German.
Title: Colour thresholds and line elements in 10 colour spaces
LABJNDu0 to 9, A0n=1/1,5
1. Introduction and goals;
2. Modifications LABJNDu0 to 9 of the colour difference formula LABJND
according to CIE 230:2019;
3. Corresponding line elements for the experimental contrast
Y/(delta Y);
4. Absolute lightness L* (CIE 15) and T* (IEC sRGB)
and relative lightness l* and t*;
5. Logarithmic and linear figures for L*, T*, l* and t*;
6. Logarithmic figures for threshold delta Y, sensitivity
(delta Y)/Y, and contrast Y/(delta Y);
7. Parameters: A0n=1/1,5, A1n=sv*cx, A2n=cv*cx, sv=0,0170, cv=0,0058, cx=1,00;
8. Variations cx=0,84, 0,67 und 0,42, and additional data.
go to the image part CEUS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part CEVS
in English or CGVS in German.
Title: Availability of ISO- and ISO/IEC-colour test charts
according to ISO/IEC 15775:2022 and ISO 9241-306:2018;
Wavelength ranges of Ostwald colours,
reflecions for 6 contrasts and antagonistic colour attributes.
1. Introduction and goals.
2. Availability and applications of ISO- and ISO/IEC-colour test charts;
3. Wavelength ranges of Ostwald colours;
4. Standard reflection R, relative reflection R1 and log(R1);
5. Triangle lightness T*;
6. Antagonistic reflections of Ostwald colours for 6 contrasts;
7. Antagonistic physiological +-signals and colour attributes.
go to the image part CEVS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part CEWS
in English or CGWS in German.
Title: Hue circle of Ostwald-optimal colours;
YN=0, YW=100, for CIE standard illuminant D65 or illuminant
P60 (6000K);
XYZ, YABCh, YABCh1, and YABCh2 data;
Data for the CIE 02 and 10 degree observer in 8 colour diagrams;
Three elementary-colour systems;
Spectral properties of optimal and surface colours;
Space coordinates: device, optimal, and Arens colours.
1. Introduction and goals.
2. Hue circle of Ostwald-optimal colours;
2.1 YN=0, YW=100, CIE standard illuminants D65, CIE 02 degree
observer;
XYZ data and 8 colour diagrams;
Data YABCh, YABCh1 and YABCh2 as table with wavelength
2.2 similar for CIE standard illuminant D65, CIE 10 degree observer;
2.3 similar for CIE illuminants P60 (6000K), CIE 02 degree observer;
3. Three elementary-colour systems
Spectral properties of optimal and surface colours;
Space coordinates: device, optimal, and Arens colours.
go to the image part CEWS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part CEXS
in English or CGXS in German.
Title: Ostwald-optimal colours;
YN=0, YW=100, for eight illuminants Dxx or Pxx;
XYZ, YABCh, YABCh1, and YABCh2 data;
Data for the CIE 02 and 10 degree observer in 8 colour diagrams;
Chromatic adaptation model for 8 Planck radiations.
1. Introduction and goals.
2. Ostwald-optimal colours;
2.1 YN=0, YW=100, 8 illuminants Dxx, CIE 02 degree observer;
XYZ data and 8 colour diagrams;
Data YABCh, YABCh1 and YABCh2 as table with wavelength;
2.2 similar for 8 illuminants Dxx, CIE 10 degree observer;
2.3 similar for 8 illuminants Pxx, CIE 02 degree observer;
3. Chromatic adaptation model
Ostwald-optimal colours for 8 Planck radiations Pxx with
8 correlated colour temperatures between 6000K (P60) and 2500K (P25).
go to the image part CEXS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part CEYS
in English or CGYS in German.
Title: CIEXYZ and LABJND data of YB(Yellow-Blue) and
GM (Green-Magenta) optimal colours
for 8 Dxx and 8 Pxx illuminants
1. Introduction and goals;
2. YB and GM data for 8 Dxx and 8 Pxx illuminants;
3. CIE 2 and 10 degree observer, CIEXYZ, LABJND, and
CIELAB data;
4. YABCabh1&2 data, wavelength lambda(1,2,d,c) of Ostwald
colours;
5. Definition of wavelength lambda1 (CEY0 to CEY3);
6. Definition of wavelength lambda1 and lambda2 (CEY4 to CEY9);
7. Performance of the calculation of lambda(2,d,c);
8. Application for the four elemetary colours RJGB.
go to the image part CEYS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part CEZS
in English or CGZS in German.
Title: Technology of images with the programming language PostScript;
Combining images (rectangle layout) to new images.
1. Introduction and goals.
2. Examples of new images in different layout;
3. Rectangular and hue circle presentation;
4. Application for the Ostwald hue circle;
5. Standard reflection R, relative reflection Rr=R/0,18 and Rs=log(Rr).
6. Wavelength limits and XYZ data of Ostwald colours for 8 illuminants.
7. Chromatic values (A, B), (A1, B1), and (A2, B2) of Ostwald colours.
go to the image part CEZS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
-------
For the start TUB web site (not archive), see
index.html in English,
indexDE.html in German.
For the archive information (2000-2009) of the BAM server
"www.ps.bam.de" (2000-2018)
about colour test charts, colorimetric calculations,
standards, and publications, see
indexAE.html in English,
indexAG.html in German.